Thinking critically about these changes, we would expect that the company has also seen a rise in sales. This quick ratio of 1.5 means that for every dollar of current liabilities, the company has $1.50 in quick assets, indicating a strong liquidity position without relying heavily on inventory. Asset turnover ratio helps assess how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate revenue. If Company C has annual revenue how to handle customer complaints the right way of $3 million and average total assets of 1 dollar million, its asset turnover ratio would be 3.0, meaning it generates 3 dollars for every 1 dollar of assets. This efficiency might reflect effective management and high demand for the company’s products. However, if industry standards show an asset turnover ratio of 4.0, Company C may need to enhance operational efficiency or increase sales to match industry performance.
Business Insights
- In this section all the resources (i.e., assets) of the business are listed.
- These obligations are classified as either current liabilities, due within the forthcoming year, or long-term liabilities, due beyond a year.
- For mid-size private firms, they might be prepared internally and then looked over by an external accountant.
- Similarly, liabilities are listed in the order of their priority for payment.
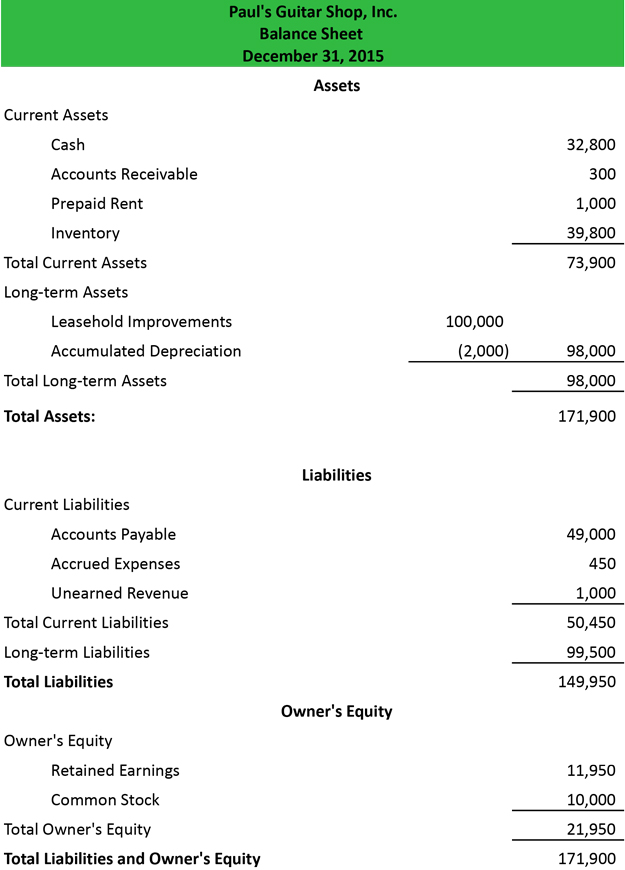
It is crucial to remember that some ratios will require information from more than one financial statement, such as from the income statement and the balance sheet. Measuring a company’s net worth, a balance sheet shows what a company owns and how these assets are financed, either through debt or equity. Investors, creditors, and internal management use the balance sheet to evaluate how the company is growing, financing its operations, and distributing to its owners. It will also show the if the company is funding its operations with profits or debt.
Balance Sheets May Be Susceptible to Errors and Fraud
Again, these should be organized into both line items and total liabilities. This will make it easier for analysts to comprehend exactly what your assets are and where they came from. Tallying the assets together will be required for final analysis. If the company wanted to, it could pay out all of that money to its shareholders through dividends. However, the company typically reinvests the money into the company. Shareholders’ equity reflects how much a company has left after paying its liabilities.
What is included in the balance sheet?
Harvard Business School Online’s Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills. Liabilities are few—a small loan to pay off within the year, some wages owed to employees, and a couple thousand dollars to pay suppliers. Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease.
Assets can be split into three sections – current assets, fixed assets, and intangible assets. Liabilities are amounts a company owes to someone else, either immediately or over a long period. One way to own a more expensive asset is by taking out a loan to pay for it, which would increase a firm’s liabilities.
PERSONAL CASH‐FLOW STATEMENT
The report provides helpful information when assessing a company’s financial stability. Financial ratios are used to calculate the business’s financial position, including liquidity and gearing ratios. Banks and suppliers use them to determine if they can offer a loan, overdraft or credit facility.

A balance sheet covers a company’s assets as defined by its liabilities and shareholder equity. One thing to note is that just like in the accounting equation, total assets equals total liabilities and equity. If you are preparing a balance sheet for one of your accounting homework problems and it doesn’t balance, something was input incorrectly. You’ll have to go back through the trial balance and T-accounts to find the error.
Take a look at these examples to give you an idea of what to include. As the name suggests, the equation balances out, with assets on the one side being equal to the sum of liabilities and equity on the other. Depending on the company, different parties may be responsible for preparing the balance sheet. For small privately-held businesses, the balance sheet might be prepared by the owner or by a company bookkeeper.
Liabilities are obligations to parties other than owners of the business. They are grouped as current liabilities and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet. Current liabilities are the obligations that are expected to be met within a period of one year by using current assets of the business or by the provision of goods or services. All liabilities that are not current liabilities are considered long-term liabilities. Liabilities and equity make up the right side of the balance sheet and cover the financial side of the company. With liabilities, this is obvious—you owe loans to a bank, or repayment of bonds to holders of debt.
